India Government Proposes Next-Gen GST Reform: Simplified Rates, Lower Car and Insurance GST
India’s GST reform 2025: Modi government proposes a two-slab GST structure, cuts taxes on small cars and insurance, and introduces a 40% sin-goods slab. Analysis with facts, figures, revenue impact, and market response
India’s tax landscape is undergoing a landmark transformation with GST 2.0, announced by Prime Minister Narendra Modi and targeted for rollout by Diwali 2025. This reform builds on the original GST launched in July 2017, aiming to simplify the structure, broaden economic inclusion, and catalyze growth.
Key Features of GST 2.0 Reform
-
Old Structure: Four major slabs—5%, 12%, 18%, 28%—plus special rates for jewelry and luxury/sin goods.
-
New Structure: Two principal slabs—5% and 18%. Special slab of 40% for luxury/sin goods (like tobacco, pan masala, high-end cars, online gaming).
-
Coverage: Essential items shift to 5%; most goods in 28% and 12% will move to lower categories, making them cheaper, especially consumer durables, FMCG, and processed foods.
-
Petroleum products, crude oil, and diamonds remain outside the GST regime.
-
Sectoral beneficiaries: Textiles, fertilizers, renewable energy, health, insurance, handicrafts, agriculture.
Additional Facts
-
Petroleum products, crude oil, and diamonds remain outside GST coverage.
-
Technology upgrades: Pre-filled returns, automated refunds, single-window registration targeted at MSMEs.
Specific Figures
-
Items shifting to lower rates:
-
Sin/Luxury Goods:
-
Revenue and Collections:
Economic and Sectoral Impact Due to Tax and GST Reforms
Impact on Key Sectors
-
Who benefits:
-
Consumers: Many everyday and aspirational goods will become cheaper.
-
MSMEs: Easier compliance, registration, and refunds.
-
Stock market: Notably, shares of companies in FMCG, auto, durables surged on the reform announcement.
-
Figures and Revenue Implications Of GST Reforms
-
Current GST Revenue Distribution: 65% from 18% slab, 11% from 28%, 5% from 12%, 7% from 5%.
-
Expected Post-Reform: Nearly 99% of items in 12% to move to 5%, and 90% in 28% to 18%. Revenue impact projected around ₹50,000 crore, considered manageable by the Finance Ministry.
-
GST Collections (Reference): January 2021 collection was ₹1,19,847 crore, up 8.15% over previous year. Post-reform, growth could accelerate with broadened taxable base and increased consumption.
Key Facts and Figures: India’s Recent GST Reforms (2025)
Major Highlights
-
New Slab Structure: GST moves from four main tax slabs (5%, 12%, 18%, 28%) to a simplified two-slab system:
-
Sectors impacted: FMCG, consumer durables, automobiles, packaged food, health and insurance, and select services all see lower taxes. Sin goods face significantly higher duties.
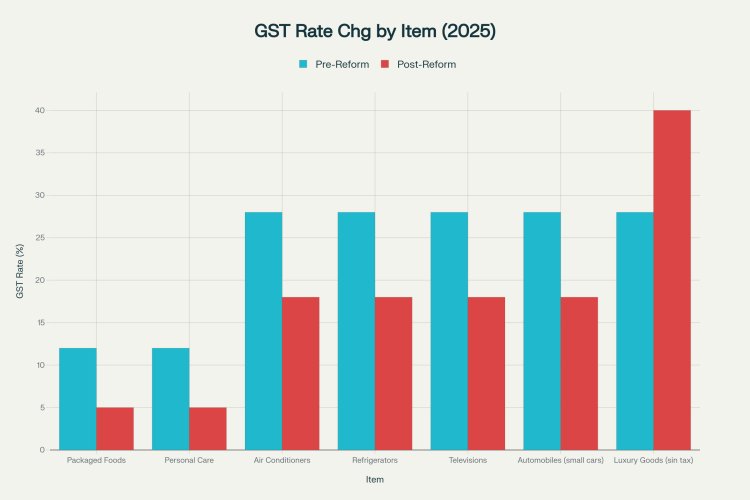
GST Rate Changes for Key Goods
Impact of 2025 GST Reforms on Key Consumer Goods: Pre- vs. Post-Reform Rates
Technology and Process Reforms
-
Registration: Seamless, tech-driven, and time-bound for small businesses, MSMEs, and startups.
-
Returns: Introduction of pre-filled returns to reduce manual errors.
-
Refunds: Automated, faster refunds for exporters and inverted duty cases.
-
Dispute Reduction: Correction of inverted duty structures and classification issues.
Social Impact
-
Common Man: Cheaper essentials, reduced financial burden.
-
Women: Lower rates on personal care, cosmetics.
-
Students: Lower taxes on educational materials and tech.
-
Middle Class: Bigger savings on durables and aspirational goods.
-
MSMEs/Startups: Reduced compliance overhead; easier registration, faster refunds.
Timeline
-
Announcement: August 15, 2025 (Independence Day).
-
GST Council Review: September 2025 (two meetings scheduled).
-
Expected Rollout: Diwali 2025.
SWOT Analysis of GST 2.0
| Strengths | Weaknesses | Opportunities | Threats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified structure | Some rates still unclear | Boost in consumption | Loss of revenue in short term? |
| Tech-driven processes | Sin tax enforcement issues | Economic growth | Black-market for luxury goods |
| Sectoral relief | Petrol/diesel still outside | Growth in MSMEs, exports | Sectoral lobbying |
| Social inclusion | Diamonds remain special | Better ease of business | Transitional confusion |
How will the new two-rate GST structure impact various sectors in India
Impact of the New Two-Rate GST Structure on Various Sectors in India (2025)
1. Consumer Goods & FMCG
-
Most Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG), packaged foods, and personal care items shift from higher slabs (12%/18%) to the 5% slab.
-
Impact: Prices drop, boosting demand and improving affordability for common households.
-
Companies: FMCG stocks and brands stand to benefit from increased volumes and lower tax outflows.
2. Consumer Durables & Electronics
-
Products like air conditioners, refrigerators, and televisions move from 28% to 18%.
-
Impact: Makes big-ticket purchases more accessible to middle-class families and first-time buyers. Manufacturers could see higher sales, potentially driving local production.
3. Automobiles (Small Cars, Two-Wheelers)
-
Small cars and economy vehicles drop from a 28% GST rate to 18%.
-
Impact: Cars become more affordable, likely leading to increased sales, especially for entry-level models and domestic manufacturers. Auto stocks surged post-announcement.
4. Sectoral Winners: Textiles, Fertilizers, Health, Insurance
-
Textiles, fertilizers, health, and insurance are expected to benefit from lower GST brackets, dropping operating costs and improving margins.
-
Impact: Health and life insurance will be accessible to a wider population; textiles and fertilizers will support agriculture and rural growth.
5. Luxury and Sin Goods
-
Goods like tobacco, pan masala, luxury cars, and online gaming now attract a 40% GST (special sin tax).
-
Impact: These products become significantly more expensive, likely curbing consumption and generating more tax revenue.
6. MSMEs & Startups
-
Compliance: Simpler rates and streamlined processes (pre-filled returns, automated refunds).
-
Impact: Lower compliance costs, easier market entry, and less paperwork, supporting entrepreneurship and small businesses.
7. Sectors With No Major Change
-
Petroleum products, crude oil, and diamonds remain outside the GST regime.
-
Impact: Their prices and tax structures remain unchanged, and sector status quo continues.
Overall Economic Impact
-
Boost in Consumption: Lower prices on most consumer goods, likely driving higher demand across sectors.
-
Stock Market: Shares in auto, consumer durables, and FMCG sectors saw strong gains on the announcement.
-
Revenue: Some short-term impact on government revenues, but anticipated net gains from expanded base and increased consumption.
India’s two-rate GST structure (2025) is set to reshape sectoral fortunes by reducing consumer costs, streamlining compliance, and ensuring targeted taxation for luxury and sin goods.
Conclusion
GST Tax Reform 2025 (GST 2.0) is expected to streamline India’s indirect tax system, boost consumer demand, reduce tax disputes, and support key sectors. By simplifying the rates to just two major slabs (5% and 18%) and imposing a high sin tax on luxury and demerit goods, the government aims to create a fairer, more accessible taxation regime. Technological updates ensure ease of living, especially for MSMEs, women, and students, furthering inclusive growth across the country.
India’s 2025 GST reforms mark a historic and ambitious overhaul, simplifying compliance and lowering costs for businesses and consumers, while putting sharper focus on revenue from luxury and sin goods.
This reform, if implemented as planned, could serve as a major catalyst for economic growth and social equity in India.

 Editor
Editor 




























